Swapping 2 numbers is one of the favorite questions asked to a lot of people during their interviews. There are a lot of ways to swap 2 numbers. In this post we have 4 methods that can be used to swap 2 numbers.
Second Method : Using multiplication and division operators
This method is simply obtained by replacing + by * and - by / operator in the above method, but this method cannot be used when one of the numbers is 0 as it involves division operation.
Third Method : Using the EX-OR operation
This method involves repeated ex-or operations between 2 numbers to swap 2 numbers. But this method can be used only for integers and cannot be used for float or double variables as bit operations for them are not defined.
Fourth Method : Using temp Variable
This is the simplest and the most common method used by a lot of people.
The Following is full C implementation of the above described methods.
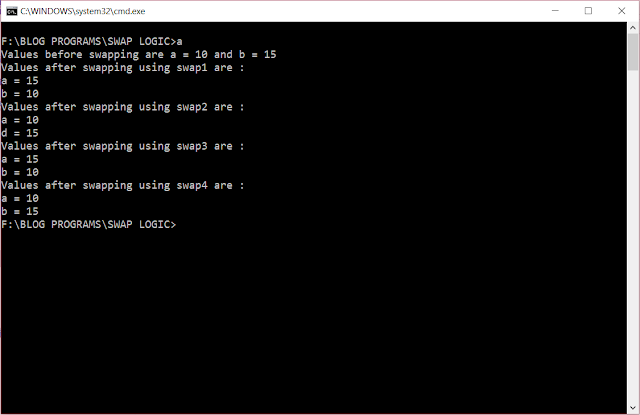
OUTPUT
You might also be interested in
Bubble Sort
Insertion Sort
Selection sort
Shell Sort
Hashing with Linear Probing
Hashing with Quadratic Probing
Double Hashing
First Method : Using addition and subtraction method
This method is a simple method that can be used to swap 2 numbers, the method can be used for all integer, float and double variables. The method involves one addition and two subtraction operations.
Second Method : Using multiplication and division operators
This method is simply obtained by replacing + by * and - by / operator in the above method, but this method cannot be used when one of the numbers is 0 as it involves division operation.
Third Method : Using the EX-OR operation
This method involves repeated ex-or operations between 2 numbers to swap 2 numbers. But this method can be used only for integers and cannot be used for float or double variables as bit operations for them are not defined.
Fourth Method : Using temp Variable
This is the simplest and the most common method used by a lot of people.
The Following is full C implementation of the above described methods.
C Program
Sample input and output to check the program
OUTPUT
You might also be interested in
Bubble Sort
Insertion Sort
Selection sort
Shell Sort
Hashing with Linear Probing
Hashing with Quadratic Probing
Double Hashing
Comments
Post a Comment